Building a New Venture in the Circular Economy
Businesses small and large face multiple challenges in today’s rapidly changing world. These stem from a variety of sources, including:
A competitive landscape that is constantly evolving
Shifting customer needs and behaviors
The rising issue of material scarcity and environmental pollution
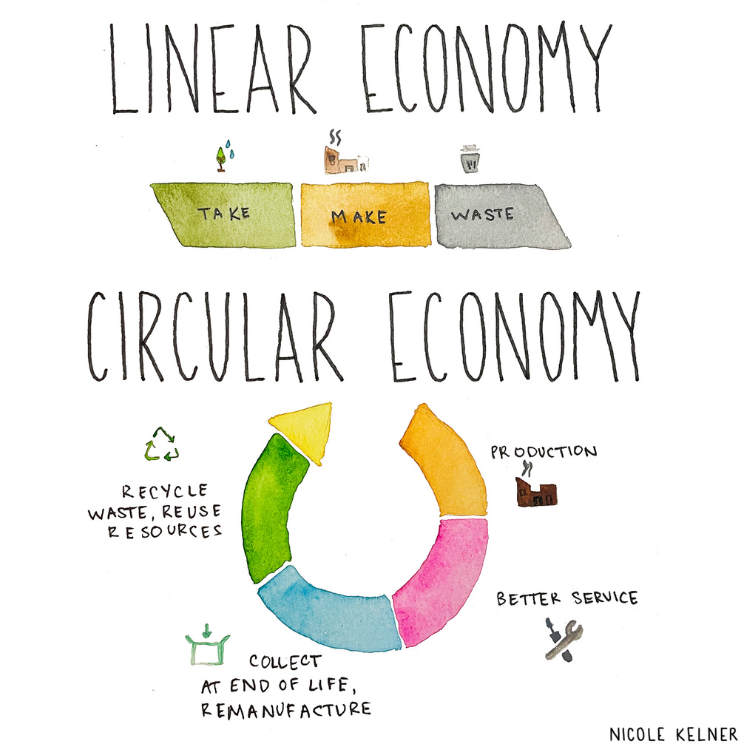
These challenges often compound if their business models are fueled by taking and selling the earth's limited resources. This is largely unsustainable in the long term, and companies that do not adapt will eventually find themselves at a competitive disadvantage.
Roughly 91% of our worldwide production of goods are not currently circular, meaning these products and materials end up in waste streams.
New companies can look to innovate towards resilient business models that create value while respecting the earth's resources. While there is no one-size-fits-all answer, we believe that circular venture building will be a major part of the solution.
Circular venture building is a new approach to business that focuses on creating value from waste and byproducts. It is based on the principles of the circular economy, which seeks to eliminate waste and pollution by keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible.
Artwork created by Nicole Kelner
Circular venture building offers a number of benefits for new companies, including:
Increased resilience: By reducing reliance on finite resources, circular businesses are more resilient to shocks and disruptions in the supply chain.
Improved profitability: Circular models can generate new revenue streams from waste and byproducts.
Reduced environmental impact: Circular businesses can help to reduce waste and pollution, which benefits the planet.
The circular economy aims to remove waste from the product life cycle and ultimately become regenerative. It does so by shifting from a take-make-waste process towards a model where material and product value is being sustained. This way, the life cycle of products is extended, waste is seen as valuable and a more efficient and resilient model is established.
By turning waste into value with new business models, companies can boost their competitiveness by reducing dependence on scarce resources and generating new innovative services that are of societal value and economically healthy.
Accenture research calculates that the global circular economy could generate $4.5 trillion of additional economic output by 2030. Launching circular ventures enables new and existing companies to tap into these value streams, strengthening their future positioning.
Although the circular economy has started to be integrated into the corporate sustainability agenda, the focus is on end-of-life management strategies, while the adoption of business models incorporating higher levels of circularity is less prevalent. In contrast, startups develop circularity strategies higher in the waste hierarchy.
Creating Circular Ventures
The below is a common pathway to launching a circular venture.
Start with an ambitious purpose: Circular ventures should be built with a clear purpose in mind. This purpose should be ambitious and should challenge the status quo. For example, a circular venture could have a purpose of eliminating waste from the fashion industry, or of expanding access to clean water for everyone.
Refine towards a circular venture-building approach: Once the purpose is clear, the next step is to refine the approach to circular venture building. This involves identifying the key value chains that need to be transformed and developing innovative solutions that can help to close the loop on materials and resources.
Envision and engage toward a circular ecosystem: Circular ventures cannot be successful in isolation. They need to be part of a larger circular ecosystem. This ecosystem can include other circular ventures, as well as governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders.
Shift from customer-centered to life-centered: Finally, circular ventures need to shift from customer-focused to product lifecycle-focused. This means thinking about the entire lifespan of a product or service, from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal of end-of-life products.
In Summary…
Circular venture building enables future-proof and effective business models. Circular ventures are designed to be more sustainable and resilient than traditional businesses. They are less reliant on finite resources and are better able to adapt to change. This makes them more future-proof and effective in the long term.
A vehicle for the necessary transition towards a circular economy. The circular economy is a way of thinking about how we produce and consume goods and services that is more sustainable and efficient. Circular ventures are a key part of this transition, as they help to reduce waste and pollution and to conserve resources.
By incorporating circular strategies such as reducing, reusing, repurposing, and recovery in venture business models, companies can be designed and scaled that thrive on sustainable value streams. Circular strategies can help companies to create more sustainable and profitable business models. For example, by reducing the amount of materials used in a product, companies can save money on raw materials and reduce their environmental impact. By reusing materials, companies can extend the lifecycle of products and avoid sending them to landfill. Repurposing can give a whole new second-life to a product - one it may not have been originally intended for. And by recovering materials, companies can extract value from waste and create new revenue streams.